Drupal Entity Translation guide

When translating content in Drupal 7, there is a choice between the i18n Internationalization package, which has been the preferred way of translating for several years, and the newer Entity Translation module.
Entity Translation operates on the field level and will be the default way of translating in Drupal 8.
Entity Translation is quite easy to configure. It has one main module and two sub modules and it doesn't provide too many options, which is good.
The biggest issue against using Entity Translation is that you still need Internationalization for certain parts of the website (like blocks). Also, the Internationalization module has more granular controls.
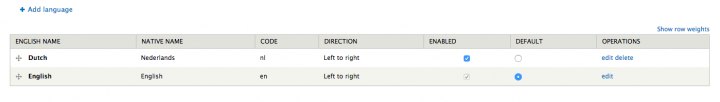
Add a language
First, we need an extra language. Go to Administration » Configuration » Regional and language » Languages and add one or more languages.
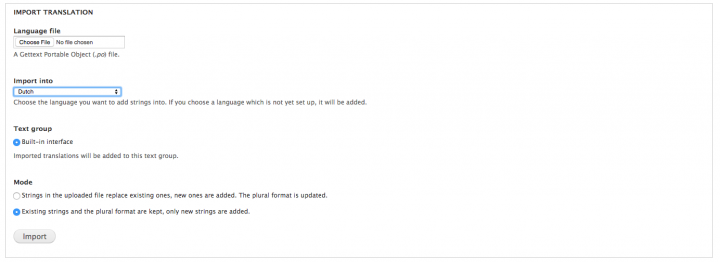
Although we have an extra language at our disposal, this language doesn't contain translated text strings; it's just an empty container. First, navigate to localize.drupal.org and download the .po language file of your choice. Go to Administration » Configuration » Regional and language » Translate interface » Import and import these text strings. This will translate the back-end but also the 'read more' buttons and the 'submitted by' text on articles on the front-end.
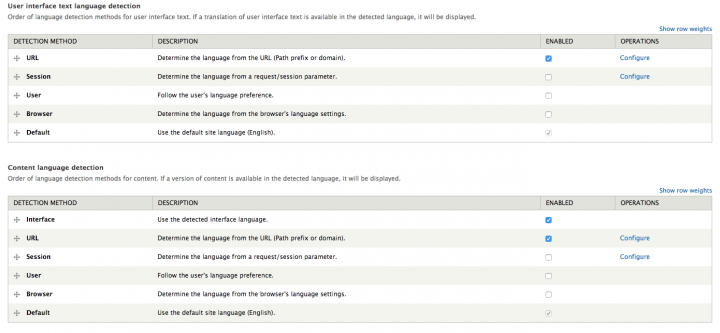
Enable detection
After enabling the Entity Translation base module, go to Administration » Configuration » Regional and Language » Languages » Detection and Selection (tab) and enable the URL setting combined with the Interface setting for a normal multilingual website. This will suit most use cases. Don't forget to put Interface and URL on top, with Interface as the first item and URL as the second.
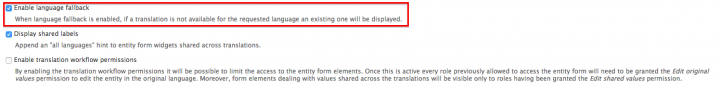
Language fallback
This setting can be found under under Administration » Configuration » Regional and Language » Entity Translation. Enabling or disabling is a personal choice. When enabled, a node without a translation, will be shown in a fallback language (in the order of languages found under /admin/config/regional/language). When disabled, an error message is shown. This error message can be visually distracting in for example Views lists.
Enable the language switcher block
Entity Translation uses the 'Language switcher (Content)' block to switch language on the front-end. The default language switcher block, 'Language switcher (User interface text)', isn't needed when using Entity Translation.
Replace default title with a field
Because Entity Translation doesn't duplicate the node (only one node ID will exist in the database, but it will be translated on the field level), we need a way to translate the title.
There is no easy way to control the title in Drupal. For example, if you want an image above the title, you would need a contrib module like Display Suite.
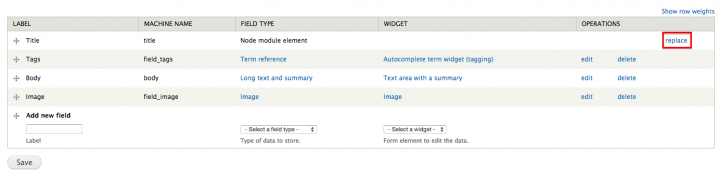
For Entity Translation, we need the Title module, which converts the title into a normal field. This field then can be translated. Click 'replace' at the field list.
Translating nodes
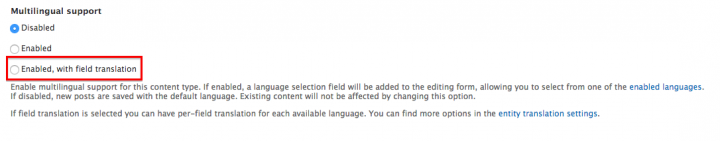
First, enable the translation on the content type. Go to the content type you want to translate (At the bottom, at the translation tab, choose 'Enabled, with field translation'.
With Entity Translation, we have granular control over the translation of every field. But we need to make every field translatable. At the bottom of every field setting, there is the option to enable or disable the translation.

A node will only exist once in the back-end. This means you have to switch the language of the back-end to English to see the English nodes.
Translating menus
Entity Translation has a sub module 'Entity Translation Menu'. It has many dependencies, like Variable and Internationalization.
Once this module is enabled, you have to go to Structure » Menus » [Name of your menu] » Edit Menu. At the bottom, check the option 'Translate and Localize'.
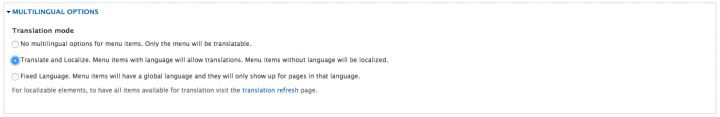
After that, every menu item can be translated.
Translating blocks
For blocks, we need the i18n sub module 'Block Languages'.
After enabling these modules, check the vertical tabs on the bottom and enable 'Make this block translatable' and pick select all the languages where the block should appear.

Now there will be a new translate tab on the top to translate the block.
If there are warnings about text formats which can't be translated, go to Administration » Configuration » Regional and language » Multilingual settings » Strings.
Translating Taxonomy
First, make sure taxonomies can be translated by Entity Translation. Go to Administration » Configuration » Regional and language » Entity Translation and enable 'Taxonomy term' under 'Translatable Entity Types'.

After that, go to the taxonomy to translate and check the fields. Notice that all the fields can be 'replaced' by a field instance. After replacing these, every field can be translated.

Translating Views
Translating Views can be done easily with Entity Translation. But you need to know how it works!
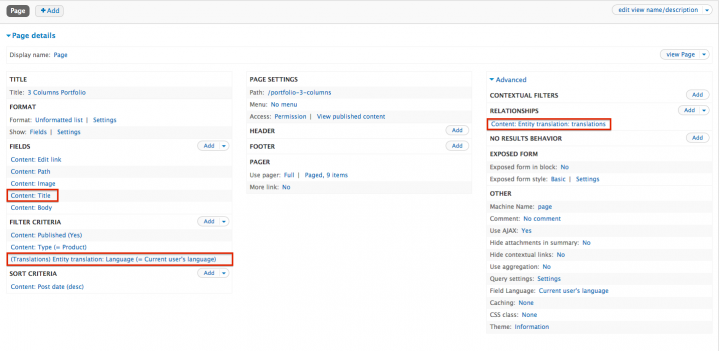
- You need to add a Entity Translation relationship (with 'Require this relationship' checked).
- You need an Entity Translation Filter, with the 'current user's language'.
- And you need to add the Title field to the fields list. The key of the title field should be title_field. You may need some guessing for the title field (they have the same human readable name) but after you have added the field you can hover over it and check the path.
When there are untranslated strings left, you have to translate them by going to Administration » Configuration » Regional and language » Translate interface » Translate.
Comments
Many thanks for this detailed
Many thanks for this detailed and useful tutorial.
Maybe a very last part on "Translating Panels"?
Greetings from France.
Thanks for the useful
Thanks for the useful information
I recommend the localization
I recommend the localization platform https://poeditor.com/ for those who want to translate Drupal sites, it is great for collaborative translation.
question, I have 2 types of
question, I have 2 types of contents, Shop and Products, both types of contents have field translation. I have entity reference field relation Products to Shop, "field_shop" in Products, I create 3 Shops w/o been translated and I create 1 Product and I related this product to the 3 Shops and I translate the product
I created 1 view bringing just the products, when i go to language 1, i get the product in language 1, then i go to language 2 and I get the the product in language 2.
I want to bring the Shop title in each Product. In Advanced View, I create a relationship with the "Entity Reference: field_shop", here i get 6 products in the language 1, when i go to language 2 i get 6 products in the language 2.
Anyone can help me ?
This is the only way making a
This is the only way making a multilingual website! Thanks a lot!
Hello there, thank you very
Hello there, thank you very much for this post that helped me a lot !
I'd like to add an extra feature for the blocks translation : you actualy can use the entity translate module with the bean block module that will allow you to perform the desirate translation one the selected block (as Bean block module allow you to create content type with fields for your blocks).
Adding relationship in views
Adding relationship in views
You need to add a Entity Translation relationship (with 'Require this relationship' checked).
Stop my site to run as query uses no index:
Using index condition; Using where; Using filesort
We have near about 50,000 nodes on site. Any way to optimise this?
else tutorial is very nice
Thanks!
Awesome thanks heaps.
Awesome thanks heaps. Especially helped so I could use the Node Limit module which is not compatible with normal Drupal translation that creates a node for each language which I was using.
www.imagineifmedia.com.au
How to show translated values
How to show translated values in views exposed filters?
Depends what you're using as
Depends what you're using as a filter. I mostly use a taxonomy as an exposed filter. In that case you have to make the taxonomy multilingual.
Add new comment